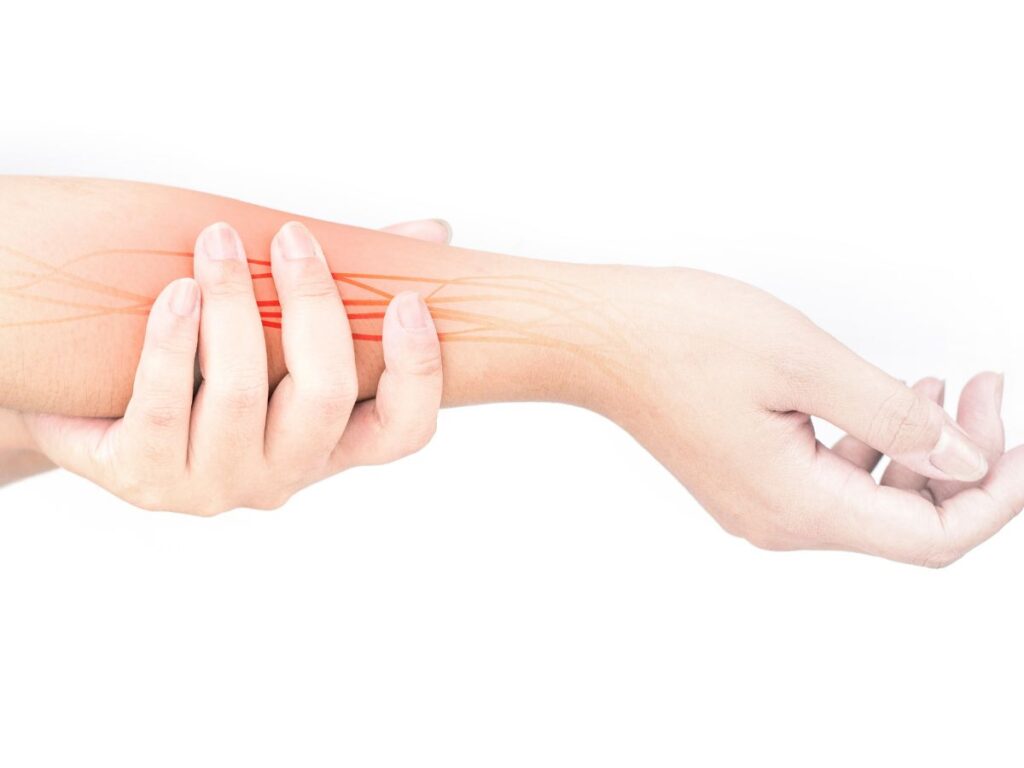
Nerve damage, or neuropathy, is a complex and often misunderstood consequence of trauma, accidents, surgery, repetitive stress, or medical conditions. When nerves are injured, patients may experience pain, weakness, tingling, numbness, or loss of function—sometimes long after the initial injury. Fortunately, modern medicine offers a range of innovative nerve damage injury therapy options to restore function, manage pain, and support healing.
How Does Nerve Damage Occur?
- Direct trauma: Car crashes, falls, sports injuries, and lacerations can physically sever or compress nerves.
- Repetitive motion: Conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or cubital tunnel syndrome result from chronic compression.
- Surgical complications: Nerves may be stretched, nicked, or compressed during procedures.
- Medical conditions: Diabetes, infections, autoimmune diseases, and tumors can also injure nerves.
Did You Know?
Peripheral nerves can regenerate at a rate of about 1 mm per day, but only under the right conditions and with proper therapy support.
Key Symptoms of Nerve Injury
- Shooting or burning pain
- Numbness and tingling (“pins and needles”)
- Muscle weakness or paralysis
- Loss of coordination or balance
- Heightened sensitivity to touch
Symptoms may appear immediately or develop slowly. Some nerve injuries recover on their own, while others require prompt intervention for the best outcome.
Modern Therapies for Nerve Damage: What Works?
1. Physical and Occupational Therapy
Therapists design customized programs to restore range of motion, rebuild strength, and retrain the brain and body. Mirror therapy, sensory re-education, balance exercises, and task-based activities are often included.
2. Medications and Pain Management
- Neuropathic pain relievers: Gabapentin, pregabalin, or duloxetine may ease burning or shooting pain.
- Topical agents: Lidocaine patches or capsaicin cream provide localized relief.
- Non-opioid and opioid options: Reserved for severe, persistent pain.
3. Nerve Stimulation and Electrical Therapies
- TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation): Noninvasive, home-based method for pain relief.
- NMES (neuromuscular electrical stimulation): Helps restore muscle activity after paralysis.
- Spinal cord or peripheral nerve stimulators: Implanted devices for chronic, severe neuropathy.
4. Surgical Solutions
- Nerve repair or grafting: Microsurgery reconnects severed nerves or bridges gaps with donor tissue.
- Nerve decompression: Frees trapped nerves (e.g., in carpal tunnel or tarsal tunnel syndrome).
- Tendon transfer: Reroutes tendons to restore lost function if nerve recovery isn’t possible.
5. Regenerative Medicine and New Frontiers
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy: Emerging treatments to support nerve regeneration.
- Low-level laser therapy: May help accelerate healing in select cases.
Personal Story: Nerve Injury Recovery in Action
After a serious wrist fracture, Sara developed numbness and weakness in her fingers—classic signs of median nerve injury. Early intervention with splinting, electrical stimulation, and supervised therapy helped her regain full movement within six months. Sara’s story highlights the value of prompt, multidisciplinary nerve damage injury therapy.
Self-Care and Home Strategies
- Follow prescribed exercises and stretches every day
- Use protective gear to prevent further injury
- Watch for new symptoms: increasing pain, muscle loss, or color changes
- Adopt a diet rich in B vitamins, antioxidants, and healthy fats to support nerve health
Myths vs. Facts: Nerve Healing
- Myth: Nerves never heal once damaged.
Fact: Many peripheral nerves can recover, especially with early intervention. - Myth: Only surgery can fix nerve damage.
Fact: Most cases improve with conservative, nonsurgical treatment.
Long-Term Outcomes and Coping
Some nerve injuries heal within weeks; others require months or years. Ongoing therapy, regular assessment, and adaptive equipment (braces, splints, ergonomic tools) can optimize daily function. For chronic symptoms, pain management and counseling help maintain independence and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Nerve Damage
- How do I know if my nerve damage is permanent? Only a specialist can determine this with tests such as EMG (electromyography) and nerve conduction studies.
- Can supplements help nerve healing? B vitamins, especially B1, B6, and B12, play a role, but always consult your provider first.
- Will I regain full sensation or strength? Many patients recover fully, but results vary by injury type, location, and timing of therapy.
When to Seek Immediate Help
If you notice rapid weakness, loss of bowel/bladder control, or severe pain and numbness spreading quickly, seek emergency care—these could signal a serious nerve or spinal cord problem.
About Dr. Elham’s Nerve Damage Injury Therapy Program
Dr. Elham’s clinic stands at the forefront of nerve damage injury therapy, integrating medical, physical, and pain management expertise. Her team develops custom care plans, drawing on advanced modalities and ongoing patient education. Whether you’re dealing with accident trauma, repetitive stress, or post-surgical complications, you’ll receive a holistic approach for your unique needs.
Your Next Steps
- Request a referral to a nerve injury specialist or neurologist
- Start therapy as early as possible for optimal outcomes
- Visit our nerve damage therapy page for more resources, tips, and guidance
Modern nerve injury therapy can restore hope and function—often when it’s needed most. With the right team and a proactive approach, recovery is within reach.